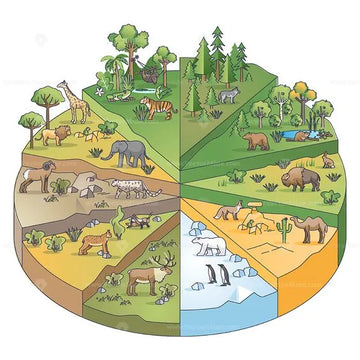
Introduction:
Welcome to the fascinating world of ecosystems! From lush rainforests to icy tundras, ecosystems encompass a diverse array of habitats teeming with life. In this blog, we'll delve into the importance, types, services, and dynamics of ecosystems, shedding light on their significance in maintaining a healthy planet.Importance of Ecosystems:
Ecosystems are the lifeblood of our planet, providing essential services that support life. They regulate climate, purify air and water, and provide habitats for countless species. Without ecosystems, life as we know it would cease to exist.Types of Ecosystems:

Marine Ecosystems:

Terrestrial Ecosystems:

Aquatic Ecosystems:

Forest Ecosystems:

Grassland Ecosystems:

Desert Ecosystems:

Rain forest Ecosystems:

Tundra Ecosystems:

Ecosystem Services:
Ecosystems provide a wide range of services that are essential for human well-being. These ecosystem services can be divided into four categories:Provisioning Services:
Provisioning services include the production of food, water, timber, and other resources that directly benefit humans. For example, forests provide timber for construction, while oceans yield seafood for consumption.
Regulating Services:
Regulating services encompass the regulation of climate, water quality, disease, and natural hazards. Ecosystems like wetlands act as natural filters, purifying water and reducing the risk of floods.
Cultural Services:
Cultural services refer to the non-material benefits that ecosystems provide, such as recreation, spiritual enrichment, and aesthetic enjoyment. Parks, beaches, and natural landmarks offer opportunities for leisure and relaxation.
Supporting Services:
Supporting services are those that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services. These include soil formation, nutrient cycling, and primary production, which form the foundation of ecosystem functioning.
Ecosystem Definition:
In ecological terms, an ecosystem is a community of organisms interacting with each other and their physical environment. This interaction forms a complex web of relationships that sustains life within the ecosystem.
Conclusion:
Ecosystems are the foundation of life on Earth, providing invaluable services that support biodiversity, climate stability, and human well-being. By understanding the importance, types, services, and dynamics of ecosystems, we can work towards preserving and restoring these vital habitats for future generations to enjoy. Join us in celebrating the wonders of ecosystems and taking action to protect our planet's natural heritage.




